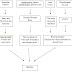
Nursing Diagnosis for Abruptio Placentae : Ineffective Tissue perfusion (peripheral)
Abruptio Placentae
Definition
Abruptio Placentae is a partial or complete detachment of the placenta from normal implantation ( corpus uteri ) after 20 weeks and before the fetus is born .
Etiology
Primary cause is not known for sure , but there are several factors that predispose
1. Factor cardio - renal - vascular
Chronic glomerulonephritis, essential hypertension, preeclampsia and eclampsia syndrome. In studies in Parkland, found that half of the cases there is hypertension in severe abruptio placentae, and half of the hypertensive women who have chronic hypertension, the rest hypertension caused by pregnancy.
2. Factors trauma
Decompression of the uterus in hydramnion and gemeli.
Pull the cord is short, due to the many fetal movement / free versions out or delivery assistance measures.
Direct trauma, such as falls, contact with kick, and others.
3. Factors maternal parity
More common in multiparous than primiparous. Some studies explain that higher maternal parity increasingly unfavorable state of the endometrium.
4. Factors maternal age
The older age of the mother, the higher the frequency of chronic hypertension.
5. Uterine leiomyoma are pregnant can cause placental abruption when the placenta implants in the upper part containing leiomyomas.
6. The use of cocaine
The use of cocaine resulted in elevated blood pressure and increased release of catecholamines are responsible for the occurrence of vasospasm uterine blood vessels and result in placental abruption. However, this hypothesis has not been proven definitively.
7. Factors smoking
Mothers who smoke also causes an increase in cases of placental disruption of up to 25 % in women who smoke ≤ 1 (one) pack per day. This can be explained in mothers who smoked the placenta becomes thinner, wider diameter and several abnormalities in the microcirculation.
8. History placental abruption before
It is very important and determines the prognosis of women with a history of placental abruption is that the risk of a repeat of this incident in a subsequent pregnancy is much higher compared with pregnant women who do not have a history of placental disruption.
9. Other influences, such as anemia, malnutrition / nutritional deficiencies, uterine pressure on the inferior vena cava due to the enlargement of the size of the uterus by the presence of pregnancy, and others.
Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions :
Ineffective Tissue perfusion (peripheral)
Definition : oxygen depletion resulting in the failure of delivery of nutrients to the tissues at the capillary level.
Defining characteristics :
- Changes in sensation.
- Changes in skin characteristics.
- Changes in blood pressure in the extremities.
- Pale skin when the elevation of the leg.
- Changes in skin temperature.
- Weak or absent pulse.
NOC :
- Circulation status.
- Fluid balance.
Expected outcomes :
After nursing action for 3x24 hours the client is able to :
1. Demonstrate the circulation status which is characterized by :
- Systolic and diastolic pressure in the normal range.
- Normal blood pressure
- Skin turgor ; not dry
NIC :
- Perform a comprehensive assessment of the peripheral circulation.
- Monitor fluid status.
- Monitor vital signs.
- Monitor cerebral perfusion pressure.
- Monitor fluid intake and output.
- Record the patient's response to stimuli.
- Position the patient in semi-Fowler's position.
- Instruct family to observe if there are lesions or skin lacerations.
- Use gloves for protection.
- Collaboration intravenous administration.
- Encourage oral input.
- Set the possibility of transfusion.
- Preparation for transfusion.
Health Education
- Teach the patient / family tenghindari extreme temperature of the extremities.
- Encourage the patient to report signs and symptoms caused.
- Encourage the patient or family to check the skin every day to determine changes in skin integrity.

.jpeg)